
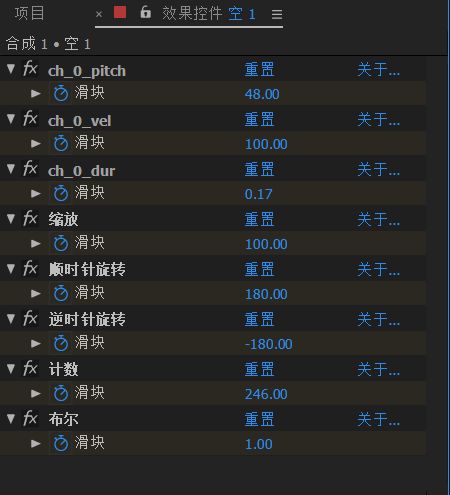
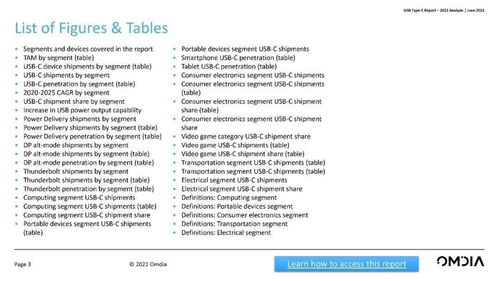
Discover the Rich Tapestry of Adjectives: A Comprehensive Guide
Adjectives are the vibrant colors that paint the canvas of language, adding depth and texture to our descriptions. They are the words that turn simple sentences into vivid images, and they are an essential part of effective communication. In this detailed exploration, we will delve into the world of adjectives, uncovering their many facets and uses.
Types of Adjectives
Adjectives can be categorized in various ways, each with its unique characteristics and applications.
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Descriptive | Describes the quality or appearance of a noun. | She has a beautiful smile. |
| Quantitative | Expresses quantity or number. | There are five apples on the table. |
| Comparative | Compares two nouns, indicating a higher or lower degree of a quality. | This book is more interesting than the last one. |
| Superlative | Indicates the highest degree of a quality. | This is the most beautiful garden in the neighborhood. |
These are just a few examples of the many types of adjectives available in the English language. Each type serves a different purpose and can be used to create a wide range of expressions.
Adjective Order
The order in which adjectives are placed in a sentence can greatly impact the meaning and clarity of the statement.
Here is a common order for adjectives:
- Size
- Age
- Shape
- Color
- Origin
- Material
- Quality
For example, “a large, old, round, red, Italian, marble, beautiful table” is a sentence that follows this order. Changing the order can completely alter the meaning of the sentence.
Adjective Agreement

Adjectives must agree in number and gender with the nouns they modify. This is particularly important in languages like German and Spanish, where adjectives must match the noun in gender and number.
In English, while adjectives do not always have to agree with the noun in number, they must match the noun in gender. For example, “the girl” requires an adjective that agrees with “girl,” such as “beautiful” or “ugly,” but not “beautifulest” or “ugliest,” as these are superlatives and not adjectives.
Adjective Clauses
Adjective clauses are groups of words that act as adjectives, providing additional information about a noun. They often begin with relative pronouns like “who,” “which,” or “that,” and are essential for creating complex sentences.
For example, “The book that you gave me is fascinating” is a sentence that uses an adjective clause to provide more information about the book.
Adjective Phrases
Adjective phrases are groups of words that act as adjectives, describing a noun. They typically consist of an adjective followed by a noun or a prepositional phrase.
For example, “a tall, dark, handsome man” is an adjective phrase that describes the man.
Adjective Usage in Different Contexts
Adjectives are used in a variety of contexts, from formal writing to casual conversation. Understanding how to use adjectives appropriately in different situations is crucial for effective communication.
In formal writing, adjectives should be used sparingly and only when necessary. Overuse of adjectives can make a piece of writing sound unprofessional and cluttered. In contrast, casual conversation often requires more adjectives to convey the desired emotion or emphasis.
Common Mistakes in Adjective Usage
Despite their simplicity, adjectives can be tricky to use correctly. Some common mistakes include:
- Misusing comparative and superlative forms
- Not using adjectives in




