
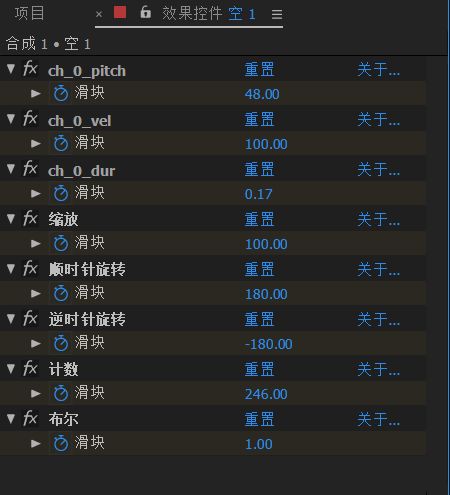
Alt Om Modernismen: A Comprehensive Overview
Modernism, a term that encompasses a wide range of artistic, architectural, and literary movements, has left an indelible mark on the world. This article aims to delve into the various dimensions of modernism, exploring its origins, key figures, and lasting impact.
Origins and Definition
Modernism emerged in the late 19th and early 20th centuries as a reaction to the industrial revolution and the perceived decline of traditional values. It sought to challenge the established norms and explore new forms of expression. While the term “modernism” is often used to describe a diverse array of movements, it generally refers to a period characterized by innovation, experimentation, and a break from the past.
Artistic Modernism
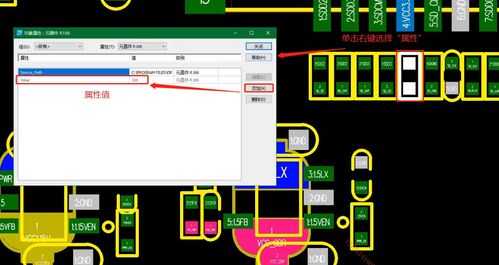
Artistic modernism encompasses various movements, including Cubism, Fauvism, Expressionism, and Surrealism. Each of these movements brought its unique approach to art, pushing the boundaries of traditional techniques and materials.
| Art Movement | Description |
|---|---|
| Cubism | Developed by Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque, Cubism broke down objects into geometric shapes and fragmented forms, creating a sense of depth and movement. |
| Fauvism | Originating in France, Fauvism emphasized vibrant colors and bold brushstrokes, aiming to convey emotions and feelings rather than realistic representation. |
| Expressionism | Expressionist artists sought to convey inner emotions and psychological states through distorted and exaggerated forms. |
| Surrealism | Surrealism explored the subconscious mind and the irrational, often resulting in dreamlike and fantastical imagery. |
Architectural Modernism
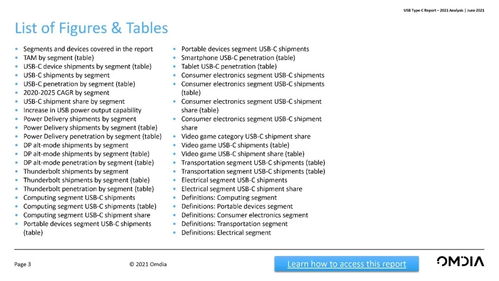
Architectural modernism, also known as modern architecture, emerged in the early 20th century and sought to create functional, efficient, and aesthetically pleasing buildings. Key figures in this movement include Le Corbusier, Ludwig Mies van der Rohe, and Walter Gropius.
One of the defining features of architectural modernism is the use of new materials, such as steel and glass, which allowed for the creation of innovative structures. The International Style, a prominent architectural movement within modernism, emphasized simplicity, geometric forms, and a lack of ornamentation.
Literary Modernism
Literary modernism refers to the movement in literature that emerged during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. It is characterized by a focus on the individual, an exploration of complex themes, and a break from traditional narrative structures.
Key literary figures of modernism include Virginia Woolf, James Joyce, and Franz Kafka. Their works often feature stream-of-consciousness narratives, complex characters, and a focus on the psychological and emotional aspects of human experience.
Impact and Legacy
Modernism has had a profound impact on the world, influencing various aspects of culture, society, and thought. Its emphasis on innovation and experimentation has inspired countless artists, architects, and writers to push the boundaries of their respective fields.
Today, modernism continues to be a source of inspiration and a testament to the human capacity for creativity and change. Its legacy is evident in the countless works of art, buildings, and literature that have emerged from this groundbreaking movement.
As you delve into the world of modernism, you’ll find that it is a rich and complex tapestry of ideas and expressions. Whether you’re an artist, architect, or simply a curious observer, modernism offers a wealth of insights and inspiration.





