
Understanding the Richness of Kannada Language
Have you ever wondered about the beauty and depth of the Kannada language? Known as one of the major languages in India, Kannada holds a significant place in the cultural and historical landscape of the country. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of Kannada, exploring its origins, script, pronunciation, and its role in the Indian subcontinent.
Origins and Evolution
The Kannada language has its roots in the ancient Dravidian language family. It is believed to have originated in the southern part of the Indian subcontinent, with its earliest inscriptions dating back to the 5th century AD. Over the centuries, Kannada has evolved, absorbing influences from various cultures and languages, making it a vibrant and dynamic language.
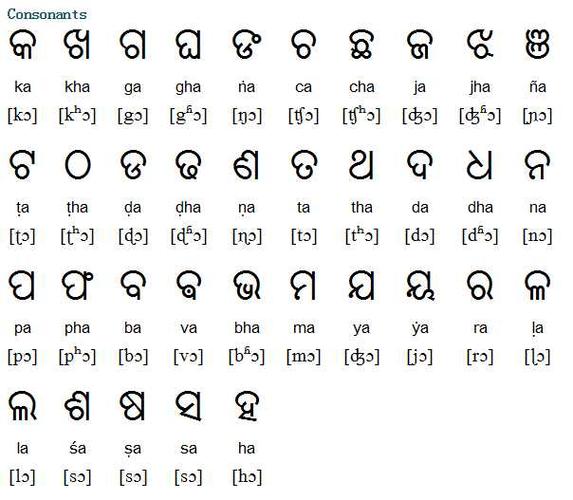
The Kannada Script
The Kannada script is a unique and beautiful writing system that has been used for over a thousand years. It is one of the oldest scripts in the world and is known for its elegance and simplicity. The script consists of 48 consonants and 14 vowels, making it a rich and expressive language. The Kannada script is also known for its distinctive characters, which are often adorned with intricate designs and patterns.
Pronunciation and Grammar
Pronouncing Kannada can be a challenge for non-native speakers, but with practice, it becomes easier. The language has a distinct rhythm and intonation, which adds to its musicality. Kannada grammar is also quite interesting, with a complex system of verb conjugations and sentence structures. Understanding the grammar rules is essential for mastering the language.
Cultural Significance
The Kannada language is not just a means of communication; it is deeply intertwined with the cultural heritage of the region. It has played a significant role in the development of literature, music, dance, and other art forms. Many renowned poets, writers, and musicians have contributed to the richness of Kannada literature and culture.
Table: Notable Kannada Writers and Their Contributions
| Writer | Contribution |
|---|---|
| Devarakshita | Considered the father of Kannada literature, wrote the first Kannada grammar book |
| Basavanna | Wrote the “Vachana Sahitya,” a collection of devotional poems |
| Subramanya | Composed the “Bhagavata Purana” in Kannada, a significant work in Hindu philosophy |
Role in the Indian Subcontinent
Kannada is one of the 22 scheduled languages in India and is spoken by millions of people across the country. It is the official language of the state of Karnataka and is widely used in neighboring states as well. The language has also gained popularity among the diaspora, with many Kannadigas living in other parts of the world preserving their cultural identity through the language.
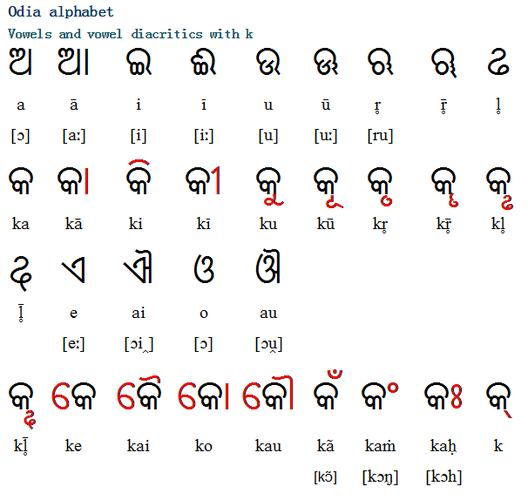
Modern Kannada
In the modern era, Kannada continues to evolve, adapting to the changing times. The language has embraced new words and phrases from English, other Indian languages, and even from the internet. This has helped in keeping the language relevant and accessible to younger generations.
Conclusion
Om Kannada is not just a language; it is a symbol of the rich cultural heritage of the Indian subcontinent. Its unique script, pronunciation, and grammar make it a fascinating language to learn and explore. Whether you are a native Kannadiga or a curious learner, understanding the beauty of Kannada can open up a world of cultural and linguistic wonders.



